Omni Family Health
Oral Cancer Screening
What is oral cancer?
Often generally referred to as “oral cancer,” oral and oropharyngeal cancers are any cancer that forms in the mouth, lips, cheeks, gums, tongue, hard palate, tonsils and throat.
Early detection is a key



Source: https://www.cancer.net/cancer-types/oral-and-oropharyngeal-cancer/statistics
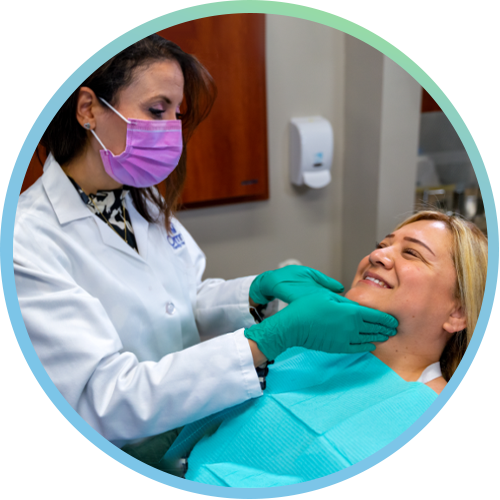

Comprehensive Oral Exam (COE)
A Comprehensive Oral Exam (COE) assesses your head and neck for anything unusual (e.g., asymmetry or abnormal lumps and bumps) and also the inside of your oral cavity. Your dentist uses their eyes (visual assessment) and their hands (palpation) to help check for anything unusual.
Although this examination is an overall assessment of the health of your head and neck region and checks for all kinds of disease, one of its most important functions is screening for oral cancer and precancer.
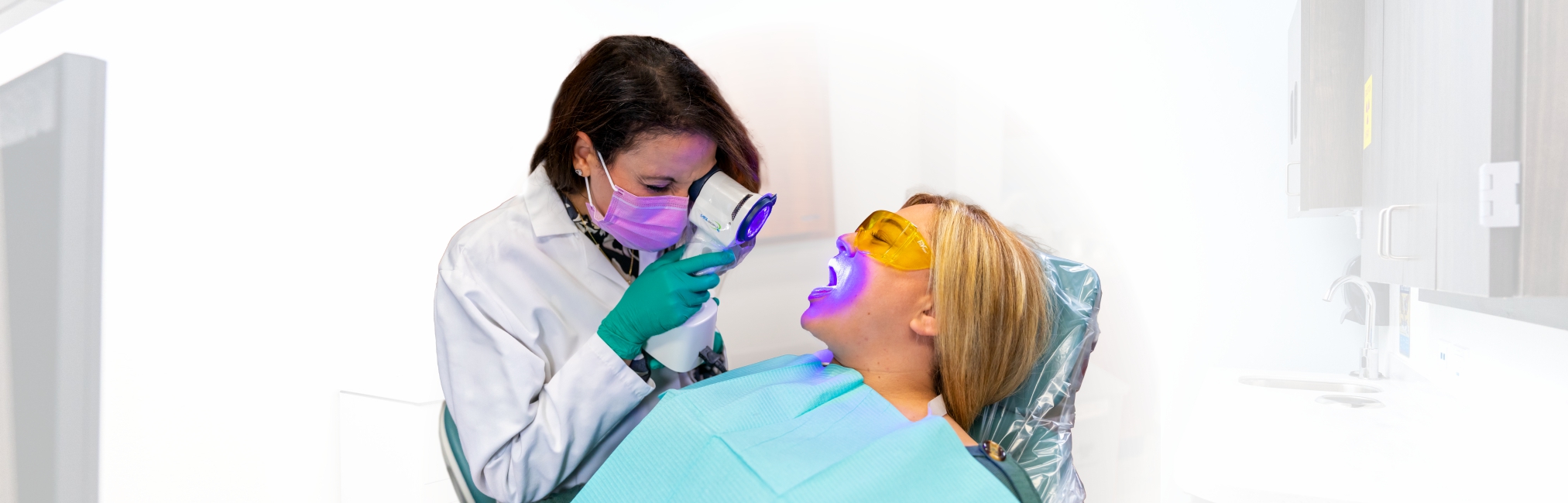
Enhanced oral screening
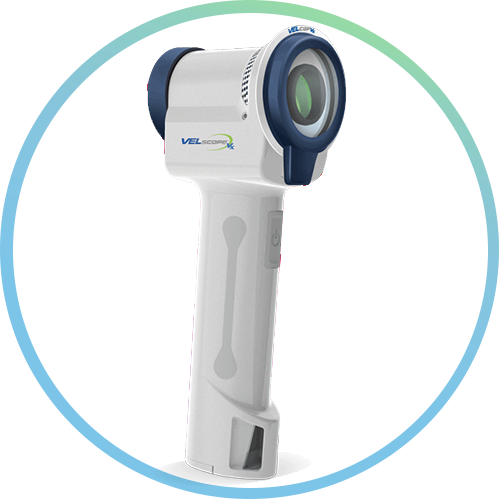
Your dentist performs an examination with the VELscope® after performing the COE to try and find anything they might have missed with the regular exam. The VELscope® emits specific wavelengths of blue spectrum light into your mouth to stimulate natural tissue fluorescence, which can be viewed directly through the VELscope®. Research has shown that the VELscope® can help find abnormal tissue that might have been unnoticed by the naked eye.

Finding an abnormality
If your dentist finds something unusual that needs further investigation, don’t panic, it doesn’t mean you have oral cancer! There are all sorts of conditions that can lead to abnormalities in your oral mucosa, and most of them are unrelated to oral cancer. Some of them will go away on their own, and some may require some sort of action on the part of the dentist to resolve.
In these circumstances, you may be asked to come for a follow-up visit so the area can be reassessed and, occasionally, your dentist may refer you to a specialist for a biopsy. Biopsy is the gold standard for diagnosing abnormal tissue.